

So it’s about a billionaire punishing intellectuals who want to reshape society?


So it’s about a billionaire punishing intellectuals who want to reshape society?


Street smarts!


Nazi Germany signed agreements with European and Soviet countries to not invade them and then did it anyways.


You ever try to put together a GUI? I absolutely get why they look like crap! Although I have been having fun playing around with egui.


Can’t recommend it enough! I’ve tried Linux distros in the past but always found that there were hardware issues or certain programs didn’t work. Not to mention I essentially had to give up gaming. Linux was cool but I just couldn’t use it as my daily driver.
I switched to Pop!_OS last month and I’ve been blown away. The install was simple and straightforward and the only hardware that required special config was my gaming mouse that needed “libratbag” and “piper” to remap the extra buttons and adjust the RGB.
Other than that, all the programs I normally use like Discord, Dropbox, Steam, and every game I’ve tested so far work flawlessly. I don’t feel like I’m missing anything or had to give up something like I did before. I actually feel like I’ve upgraded since I’m loving the auto tiling window manager and multiple desktops that Pop!_OS has as options.


You’re copying the idea of brilliant entrepreneur Chabuddy G.



It’s probably just that people in those countries prefer their erotic comics to be short and to the point. The chart even has a bar for “speechless” so I don’t think language density has much to do with page count. There’s also a bar for “translated” which seems to show translators pick shorter comics, which is interesting.
Here’s a excerpt from man chmod that can be summarized as “You probably want to mark the file you downloaded as executable. Run chmod +x FILENAME”
DESCRIPTION
This manual page documents the GNU version of chmod. chmod
changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode,
which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make,
or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode
bits.
The format of a symbolic mode is [ugoa…][[-+=][perms…]…], where perms is either zero or more letters from the set rwxXst, or a single letter from the set ugo. Multiple symbolic modes can be given, separated by commas.
A combination of the letters ugoa controls which users’ access to the file will be changed: the user who owns it (u), other users in the file’s group (g), other users not in the file’s group (o), or all users (a). If none of these are given, the effect is as if (a) were given, but bits that are set in the umask are not affected.
The operator + causes the selected file mode bits to be added to the existing file mode bits of each file; - causes them to be removed; and = causes them to be added and causes unmentioned bits to be removed except that a directory’s unmentioned set user and group ID bits are not affected.
The letters rwxXst select file mode bits for the affected users: read ®, write (w), execute (or search for directories) (x), execute/search only if the file is a directory or already has execute permission for some user (X), set user or group ID on execution (s), restricted deletion flag or sticky bit (t). Instead of one or more of these letters, you can specify exactly one of the letters ugo: the permissions granted to the user who owns the file (u), the permissions granted to other users who are members of the file’s group (g), and the permissions granted to users that are in neither of the two preceding categories (o).
A numeric mode is from one to four octal digits (0-7), derived by adding up the bits with values 4, 2, and 1. Omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros. The first digit selects the set user ID (4) and set group ID (2) and restricted deletion or sticky (1) attributes. The second digit selects permissions for the user who owns the file: read (4), write (2), and execute (1); the third selects permissions for other users in the file’s group, with the same values; and the fourth for other users not in the file’s group, with the same values.
chmod doesn’t change the permissions of symbolic links; the chmod system call cannot change their permissions on most systems, and most systems ignore permissions of symbolic links. However, for each symbolic link listed on the command line, chmod changes the permissions of the pointed-to file. In contrast, chmod ignores symbolic links encountered during recursive directory traversals. Options that modify this behavior are described in the OPTIONS section.


You want me to find illegally trafficked wildlife? What do I look like? A giant rat??


The existence of “echo chambers” is debated by scientists. It really doesn’t matter who you hang around with, you’re going to disagree with people.
The echo chamber is overstated: the moderating effect of political interest and diverse media.
Tweeting from left to right: Is online political communication more than an echo chamber?
Hello,promitheas
Welcome to Linux Community.
It sounds like you are experiencing some quality issues using Microsoft forums, could you please provide some details to let us assist you better:
1->General System Information: Could you provide some details about your PC’s hardware specifications? Specifically, the processor, amount of RAM, and the graphics card you are using.
2->System File Check: When you say you automatically checked system files, did you use the built-in System File Checker (SFC) tool? Did it report any issues, or did it indicate that everything was fine?
3->Event Viewer: In the Event Manager, can you provide more specific details about the critical errors you see? For example, the exact error messages and any associated error codes.
Have you researched the specific error messages you found in the Event Manager (e.g., Application Error, Application Hang, Windows Error Reporting, DbxSvc, DistributedCOM, nvlddmkm)? Understanding these errors can often provide clues about the root cause of the problem. In the meantime, are you getting a blue screen on your device, and if it’s convenient, try to see if a small dump file has been generated in the corresponding path, which you can upload and share with me-<Read small memory dump files - Windows Client | Microsoft Learn>
4->Cooling and Hardware Issues: Have you noticed any unusual temperature increases while running games or any other hardware-related issues like unusual fan noises or system freezes?
5->Rollback to Previous Windows Version: If the issue started immediately after switching to Windows 11, have you considered rolling back to your previous Windows version temporarily to see if the crashes persist?
The five points of detail above are intended to give me a better understanding of the situation so that I can give potential advice and solutions.
Best regards,
ImplyingImplications |Microsoft Community Support Specialist


puts probes of voltmeter into outlet
I’m in.


Just another billion parameters bro! I swear if we add another billion it’ll fix everything!


no Swedish law is being violated
Unfortunately, Swedish courts disagreed
Windows, Mac, or Linux?
There is another…
Can you make it do this?
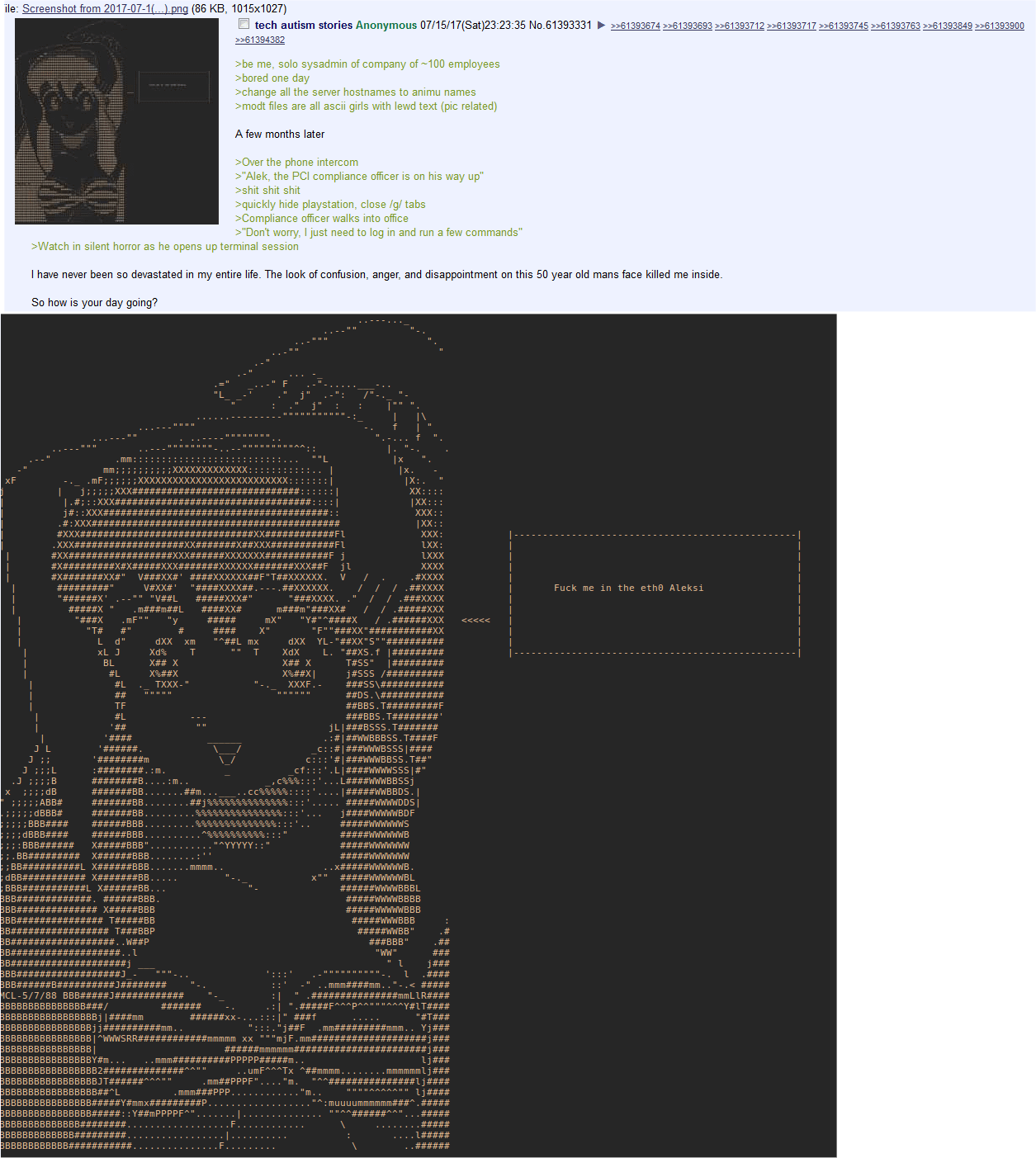
Vine…forgotten…
The porn. Right now the porn subreddits are mostly advertising for subscription sites like OnlyFans, Fansly, Patreon, etc. Reddit definitely thinks they can stop being used to advertise subscription sites and just become one themselves.